Industrial Fume Extraction Systems
Fume extraction systems help protect worker’s health by filtering and removing harmful gases, fumes, and particulate. This process is essential in machine shops, welding, metalworking, injection molding, additive manufacturing, and chemical processing workspaces.
Applications
- Welding
- Grinding and Metalworking
- Additive Manufacturing
- Plastics
- Chemical Processing


Brands
- Donaldson Torit
- Plymovent
- IVEC Systems
- Nederman
How Do Fume Extraction Systems Work?
A fume extractor is a system that utilizes a fan using induced draft, or negative pressure, to pull fumes and particulate into a contained filtration system. As the air passes through a series of filters, it removes toxic chemicals and hazardous particles from the air in the workspace. The hazardous fume particulates are collected within the filters. At the end of the process, clean air is either expelled from the building or recirculated to the workspace.
Many industries rely on fume extraction to keep workers safe from hazardous particles, such as welding, grinding, sanding, thermal spraying, plasma cutting, and any other processes that create exhaust fumes. Without fume extraction systems, the workers, machinery, and workspace would not be protected and safe.
OSHA and Other Safety Regulations
The performance of fume extractors are regulated by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), and other state and local regulations. Because fumes containing metallic particulate and other carcinogens can be 50 to 75 times smaller in diameter than a human hair, they are easy to inhale. Poor ventilation and fume extraction can lead to inhalation of hazardous fumes, which can cause respiratory diseases.
Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs)
OSHA sets different permissible exposure limits for different types of metals. The level of particle filtration and extraction required for your shop will depend on what metals or particulates workers are exposed to.
For aluminum, iron, and mild steel, the PEL is 5 milligrams of particulates per cubic meter of air (5 mg/m3) averaged over an 8-hour period. More toxic metals such as chrome, manganese, stainless steel, nickel, and cadmium, have stricter PELs.
For each workplace, consult local and state regulations for specific permissible exposure limits.
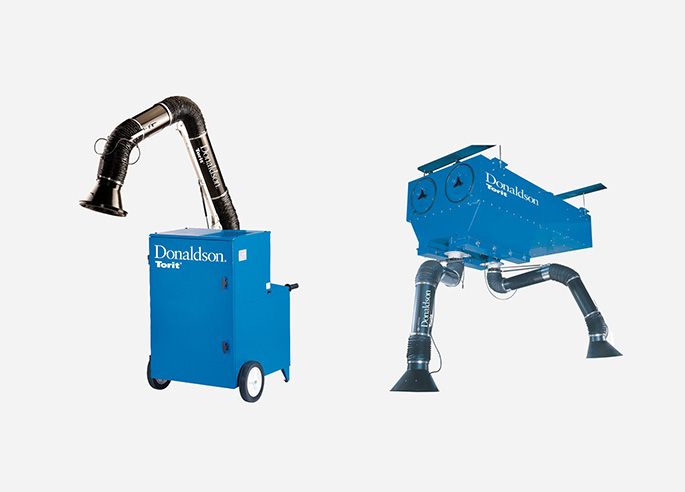
Types of Fume Extractors
Some varieties of fume extractors are fixed fume extraction systems, movable (or portable) fume extractors, benchtop fume extractors, downdraft tables, and extraction hoods.
Types of Fume Extraction Filters
| Type | Efficiency | Size of Particulates |
|---|---|---|
| ASHRAE | 95% | 0.5 microns |
| HEPA | 99.97% | 0.3 microns |
| ULPA | 99.995% | 0.12 microns |
| Micro-Pleat | 95% | 0.3 microns |
Don’t See What You’re Looking For?
Other Custom Solutions Are Available
Contact an applications specialist to get help with an air filtration solution for your facility or plant.